Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2020; 115(6): 1184-1189
The Role of the Endothelium in Severe COVID-19
Introduction
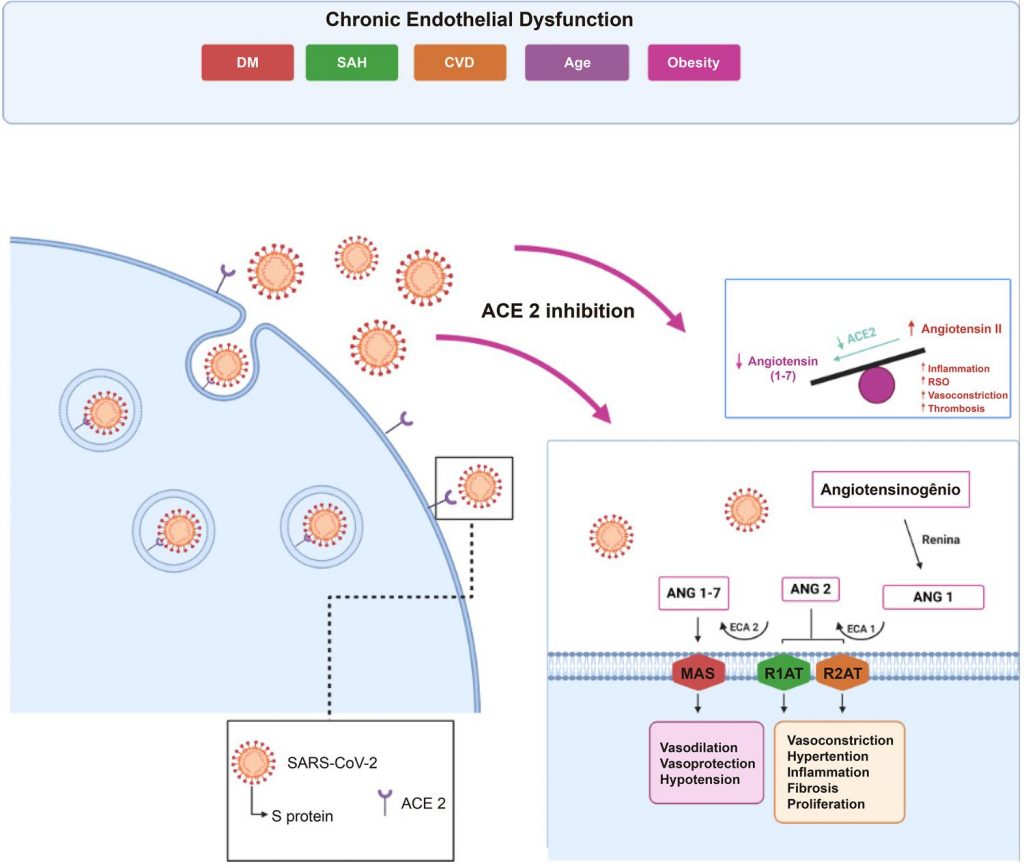
Studies have unveiled a significant link between the severity of COVID-19 ( CO rona VI rus D isease 2019) and immune markers. It is well-known that the endothelium participates actively in the immune response and interacts closely with the coagulation system. Chronic inflammatory processes of the endothelium are involved in the physiopathology of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and metabolic diseases. These diseases can negatively impact the evolution of COVID-19 and an exacerbated immune response of the endothelium seems to be a determining factor of this effect.
Coronavirus 2 of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV-2) causes infection by means of the link of the S protein to the Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE 2) on the surface of human cells. In this sense, a reduction in the availability of this enzyme can be observed, which is widely expressed in a number of bodily tissues, most notably, the lungs, heart, and endothelium, with a disorder in the modulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Consequently, what can be seen is a favoring of the greater concentration of angiotensin 2 with a series of deleterious actions against our organism. Conditions associated with the chronic dysfunction of the endothelium, such as age, systemic arterial hypertension (SAH), CVD, diabetes, and obesity are the most common in patients with severe COVID-19 ( ). ,
[…]
1,735