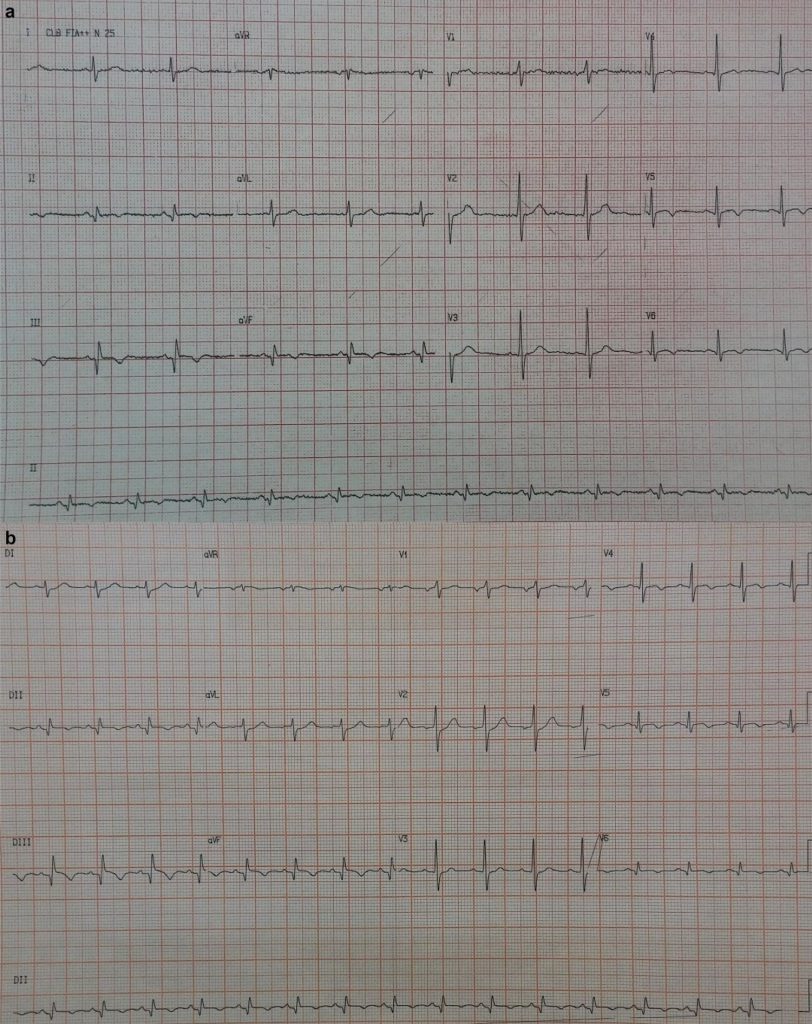
Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2020; 114(4 suppl 1): 27-30
Acute Myocardial Infarction as First Onset of Polycythemia Vera
Introduction
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a chronic clonal progressive myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by an absolute increase in erythrocytes and, usually, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, and splenomegaly. Its incidence rates around 2.8/100,000 people per year. Diagnosis is confirmed using the criteria defined by the 2016 revised World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines. Major criteria include hemoglobin levels over 16.5 and 16.0 g/dL or hematocrit over 49 and 48% in men and women, respectively, or increased red cell mass of more than 25% above the mean normal predicted value; bone marrow biopsy showing hypercellularity for age with trilineage growth; presence of JAK2V617F or JAK2 exon 12 mutation. A minor criterion is reduced serum erythropoietin level. Diagnosis requires meeting either all 3 major criteria or 2 major criteria and the minor criterion. The patient is also considered as at thrombosis risk; those aged over 60 or with thrombosis history are considered at considered high risk; if both risk factors are absent, low risk is considered.
Treatment includes cytoreductive drugs, such as hydroxyurea, antiplatelet agents and therapeutic sangrias.
[…]
1,208