Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2024; 121(10): e20240128
Assessment of Pulmonary Congestion According to Ultrasound and Remote Dielectric Sensing (ReDS) in Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Impact of Technological Innovation in the Treatment and Prognosis of Heart Failure".
Abstract
Background
The reduction of pulmonary congestion is an essential clinical target in the management of chronic heart failure. The remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) system is a recently introduced non-invasive technology used to easily estimate the degree of lung fluid volume without any expert techniques.
Objective
To conduct a comparative assessment of pulmonary congestion according to ultrasound and ReDS technology in patients hospitalized with decompensation of chronic heart failure (CHF)
Methods
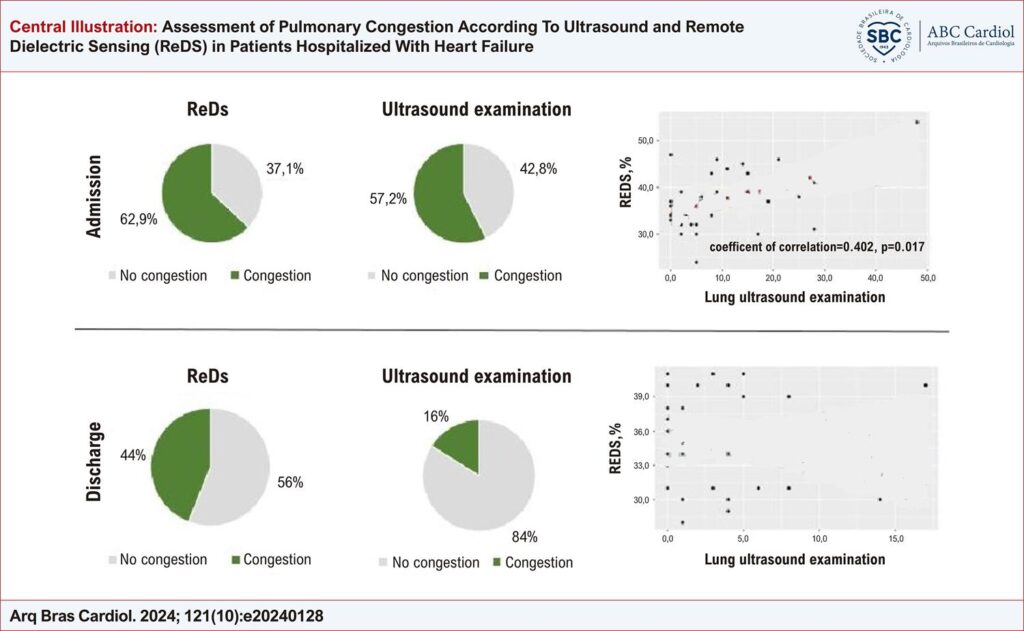
The pilot single-center study included patients hospitalized with CHF decompensation. On admission and upon discharge, lung ultrasound and ReDS technology were simultaneously performed. Ultrasound of the lungs was performed according to the protocol with an assessment of 8 zones and calculation of the sum of B-lines. Pulmonary congestion was confirmed with a sum of B-lines ≥5, ReDS congestion if >35%. A p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
35 patients were included in the study; 40% (n=14) were men, the average age was 71 (65.5; 78.5) years. Pulmonary congestion, according to ultrasound, was 57.1% (n=20), and according to ReDS, 62,9% (n=22). A moderate correlation was found between ReDS (%) and lung ultrasound (sum of B-lines) upon admission (Spearman correlation coefficient = 0.402; p=0.017). There was no correlation between the two methods at discharge (p=0.613).
Conclusion
There was a moderate correlation between ReDS and lung ultrasound in relation to the detection of pulmonary congestion at admission.
Keywords: Heart failure; Pulmonary Edema; Ultrasonography
568