Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2022; 119(3): 402-410
Assessment of the Relatıonshıp Between the Adropın Levels and the Coronary Collateral Cırculatıon in Patıents wıth Chronıc Coronary Syndrome
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Another Player in Increasing Collateral Circulation in the Heart – Another Potential Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Medicine?".
Abstract
Background
Coronary collateral circulation (CCC) provides an alternative blood flow to myocardial tissue exposed to ischemia and helps to preserve myocardial functions. Endothelial-derived nitric-oxide (NO) production and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have been suggested as the most important factors in the development of CCC. Adropin is a peptide hormone responsible for energy hemostasis, and is known for its positive effects on the endothelium through NO and VEGF.
Objective
The aim of this study is to investigate the association between adropin and the presence of CCC in patients with chronic coronary syndrome (CCS).
Methods
A total of 102 patients with CCS, who had complete occlusion of at least one major epicardial coronary artery, were included in the study and were divided into two groups: the group of patients (n:50) with poor CCC (Rentrop 0-1) and the group of patients (n:52) with good CCC (Rentrop 2-3). The level of significance adopted in the statistical analysis was 5%.
Results
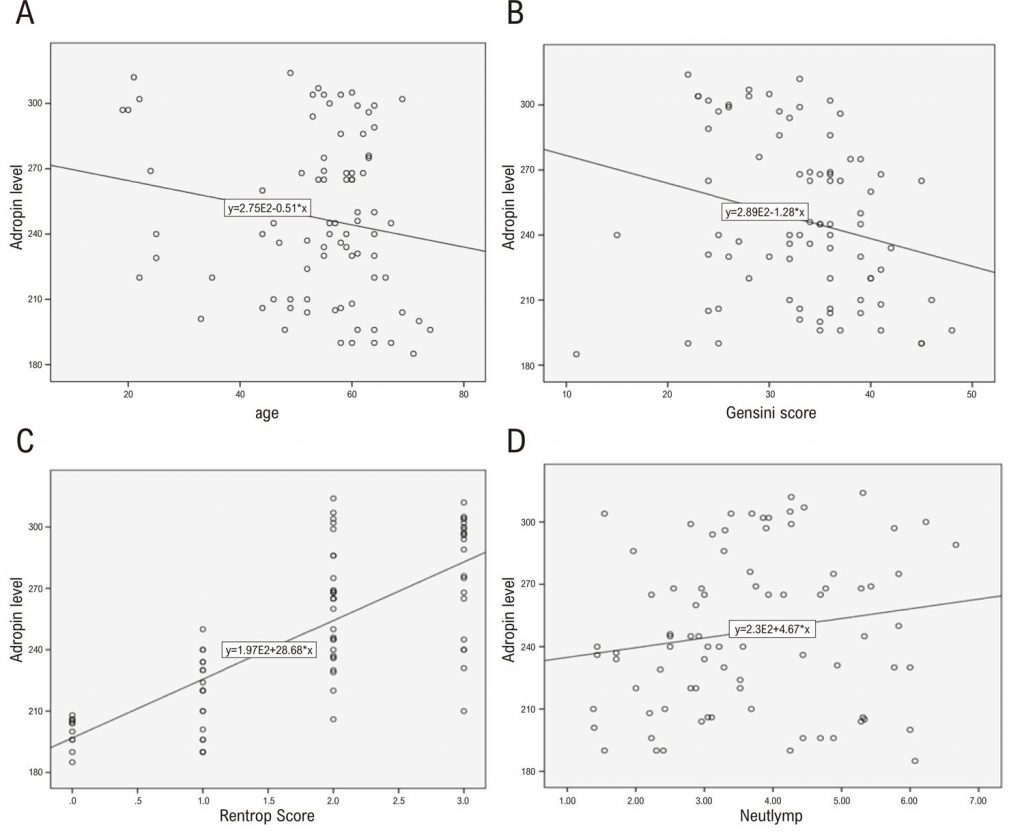
Mean adropine levels were found as 210.83±17.76 pg/mL and 268.25±28.94 pg/mL in the poor and good CCC groups, respectively (p<0.001). Adropin levels proved to be positively correlated with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios (r:0.17, p:0.04) and the rentrop scores (r:0.76, p<0.001), and negatively correlated with age (r:-0.23, p:0.01) and Gensini scores (r:-0.19, p:0.02). Adropin level is a strong independent predictor of good CCC development (OR:1.12, 95% CI:(1.06–1.18), p<0.001).
Conclusion
This study suggests that adropin levels may be a possible factor associated with the presence of CCC in CCS patients.
662