Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2023; 120(7): e20220728
Association between Arterial Hypertension and Laboratory Markers, Body Composition, Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Autonomic Parameters in Obese Patients
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Obesity-Induced Hypertension".
Abstract
Background
Systemic arterial hypertension (SAH) is a multifactorial disease, highly prevalent and associated with health risks.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between SAH and laboratory, anthropometric, heart rate variability (HRV), and obstructive sleep apnea markers and, secondarily, to analyze the sensitivity and specificity of the variables that are independent factors in the association.
Methods
Cross-sectional study with 95 obese patients treated at an obesity referral clinic in Salvador, BA, Brazil. SAH data were obtained from electronic medical records. The sample was stratified in the Normotensive Group (NG) and the Hypertensive Group (HG), and laboratory markers, body composition, polysomnography, and HRV were measured to evaluate the association of SAH with the predictor variables. For the analysis, p<0.05 was adopted.
Results
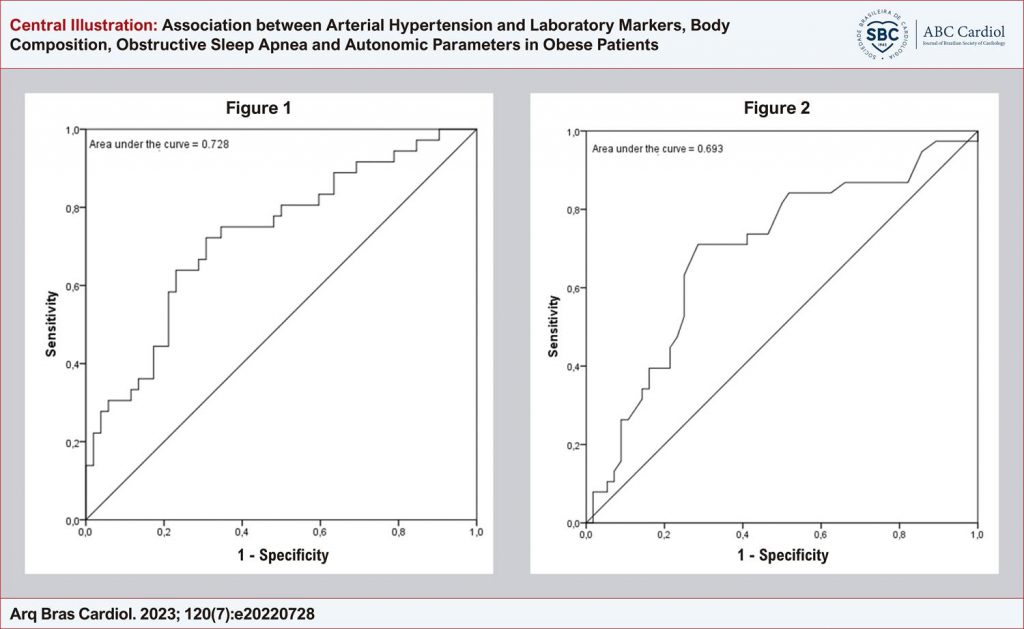
The average age of the NG was 36.3 ± 10.1 and HG 40.4 ± 10.6 years; 73.7% were women in the NG and 57.9% in HG; 82.4% in HG had insulin resistance. In the multivarious logistics regression model with adjustments in age, sex, height, and oxyhemoglobin saturation, SAH was inversely associated with fasting plasma glucose mg/dL (odds ratio [OR] = 0.96; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.92-0.99) and visceral fat area (VFA) cm2(OR = 0.98; 95% CI = 0.97-0.99). The area under the VFA curve was 0.728; CI 95% (0.620-0.836); fasting plasma glucose 0.693;CI 95% (0.582-0.804).
Conclusions
Lower VFA and fasting plasma glucose concentrations were inversely associated with SAH. In addition, fasting plasma glucose and VFA showed a high sensitivity for SAH screening.
Keywords: Adults; Biomarkers; Body Composition; Heart Rate; Hypertension; Obesity; Sleep Apnea, Obstructive
1,631