Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(8): e20240869
Association between Glucose/lymphocytes Ratio and Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Myocardial Infarction without Diabetes Mellitus
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Inflammation and Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: The Emerging Role of the Glucose-to-Lymphocyte Ratio".
Abstract
Background
Glucose metabolism and systemic inflammation appears to be strongly related to many cardiovascular diseases. Glucose to lymphocyte ratio (GLR), a novel promising marker, has been recognized as a reliable predictor of prognosis in various cancers. However, there are still no studies on the association of cardiovascular disease with GLR.
Objectives
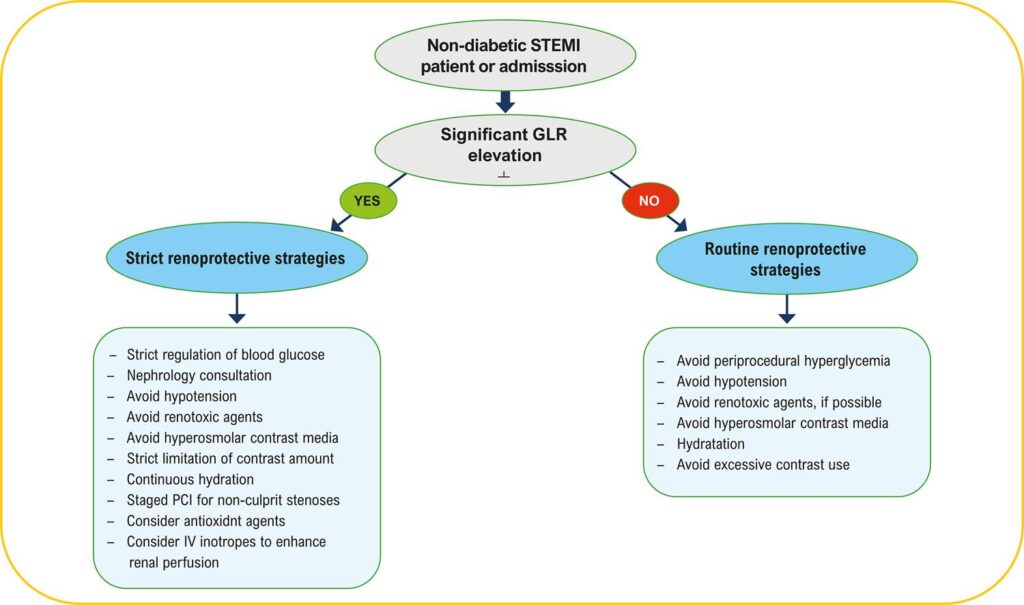
This analysis aimed to uncover the potential association between GLR and the risk for contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) after primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) in a ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI) population.
Methods
Clinical data of 592 nondiabetic STEMI patients managed with PPCI from February 2021 to February 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. Patients with end-stage kidney disease, missing laboratory data, cancers, inflammatory/infectious diseases, or died during the procedure or within 24 hours after the procedure were excluded. The receiver operating characteristic curve was used to determine the optimal cutoff of GLR in CI-AKI. Based on the cutoff value, the study population was categorized into high-GLR (≥4.16) and low-GLR (<4.16) groups. The level of significance adopted in the statistical analysis was 5%.
Results
The overall CI-AKI incidence was 7.4%. The high-GLR group showed a higher CI-AKI incidence in comparison to the low-GLR group (30.9%vs1.3%, p<0.001). Following adjustment for potential confounders, high-GLR still served as an independent predictor for CI-AKI (odds ratio [OR] 45.100, 95% confidence interval [CI] 7.312-278.174, p<0.001), as well as creatinine at admission (OR:10.459, 95%CI 1.169-93.583, p=0.036).
Conclusions
In conclusion, a high GLR level served as an independent risk factor for CI-AKI evolution after PPCI in subjects with STEMI without diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury; Contrast Media; Myocardial Infarction
184