Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(7): e20250012
Association of Endothelial Activation and Stress Index with Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-cause Mortality in Patients with Osteoarthritis
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Applying EASIX in Osteoarthritis. The Link between Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risk".
Abstract
Background
Osteoarthritis is a prevalent type of arthritis characterized by chronic degenerative changes in the musculoskeletal system, which can result in joint damage and chronic pain.
Objective
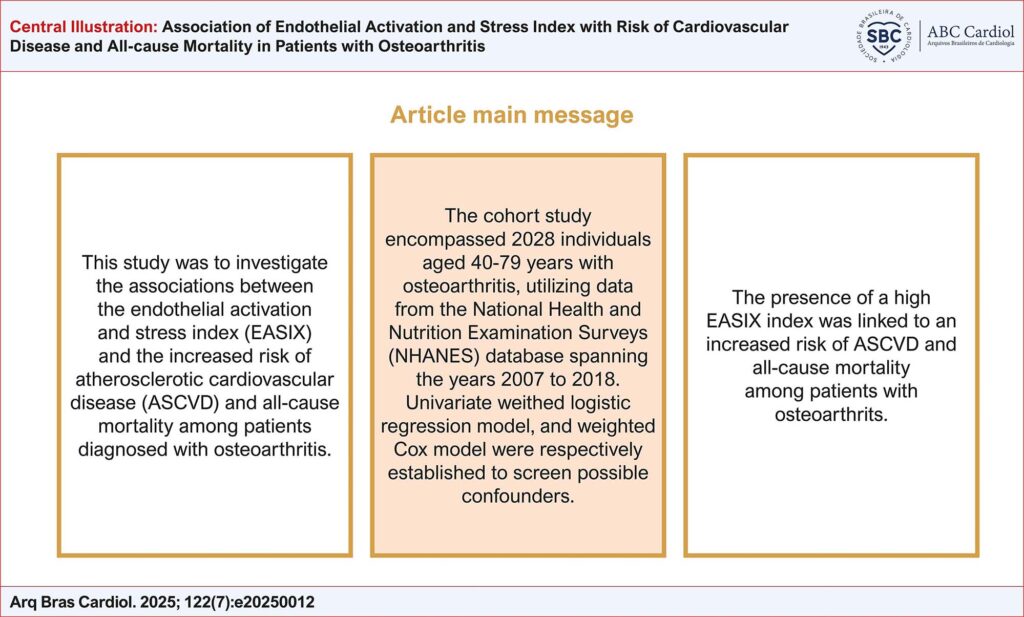
This study was to investigate the associations between the endothelial activation and stress index (EASIX) and the increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and all-cause mortality among patients diagnosed with osteoarthritis.
Methods
The cohort study encompassed 2028 individuals aged 40-79 years with osteoarthritis, utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) database spanning the years 2007 to 2018. The univariate weighted logistic regression model and weighted Cox model were respectively established to screen possible confounders. A significance level of p < 0.05 was adopted for all statistical analyses.
Results
The study revealed an elevated risk of ASCVD in correlation with an increased log (EASIX) (Odds Ratio: 1.94, with 95% Confidence Interval:1.57-2.41). When compared to individuals with log (EASIX)< -1.29, those with a log (EASIX) > -0.78 demonstrated a heightened risk of ASCVD (Odds Ratio: 2.31, with 95% Confidence Interval:1.68-3.18). A higher log (EASIX) value was also linked to an increased risk of mortality from all causes (Hazard Ratio: 1.59, with 95% Confidence Interval:1.14 -2.23). Among individuals diagnosed with osteoarthritis, those exhibiting log (EASIX)> -0.78 faced a greater risk of dying from any cause, as compared to patients with log (EASIX) <-1.29.
Conclusion
The presence of a high EASIX index was linked to an increased risk of ASCVD and all-cause mortality among patients with osteoarthritis.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Diseases; Mortality; Osteoarthritis
160