Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2022; 119(2): 294-304
(-)-Carvone Modulates Intracellular Calcium Signaling with Antiarrhythmic Action in Rat Hearts
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Where are We Going with Natural Products? Exploring the True Potential of New Plant-Based Drugs in the Cardiovascular Field".
Abstract
Background:
(-)-Carvone is a monoterpene found in essential oils with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity.
Objective:
The aim of this paper was to analyze the antiarrhythmic property of (-)-carvone in the rat heart and its effects on the intracellular Ca2+ signaling.
Methods:
The effects of (-)-carvone were evaluated on the ventricular (0.5 mM) and atrial contractility (0.01 – 4 mM) and on electrocardiogram (0.5 mM). Fractional shortening, L-type calcium current (ICa,L) and Ca2+ signaling were measured in the isolated cardiomyocyte (0.5 mM). Antiarrhythmic effect was evaluated in arrhythmia model induced by calcium overload (0.5 mM) (n = 5). P < 0.05 was used as the significance level.
Results:
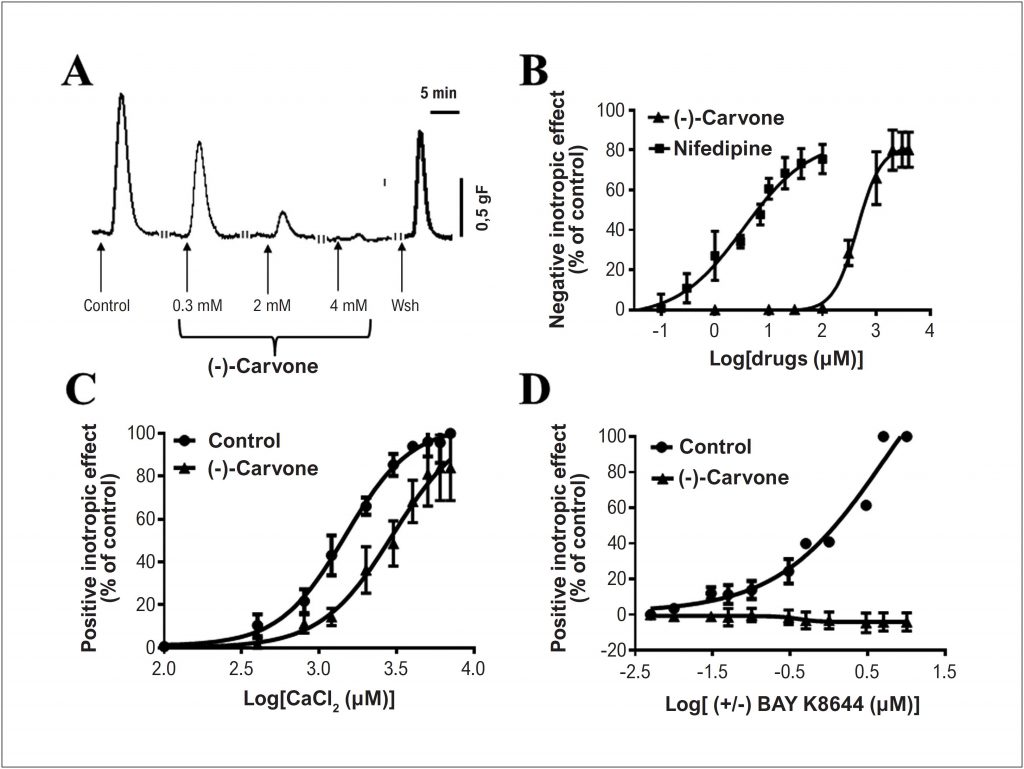
In the atrium, (-)-carvone evoked negative inotropism that was concentration-dependent (EC50 0.44 ± 0.11 mM) and decreased the positive inotropism evoked by CaCl2 (0.1 to 8.0 mM) or BAY K8644 (5 to 500 nM), an agonist of L-type Ca2+ channel. In isolated heart, (-)-carvone (0.5 mM) promoted reduction of ventricular contractility (73%) and heart rate (46%), increased PRi (30.7%, time from the onset of the P wave until the R wave) and QTc (9.2%, a measure of the depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles) without changing the QRS complex duration. (-)-Carvone decreased the fractional shortening (61%), ICa,L (79%) and Ca2+ intracellular transient (38%). Furthermore, (-)-carvone showed antiarrhythmic action, verified by decrease of the arrhythmia score (85%) and occurrence of ventricular fibrillation.
Conclusion:
(-)-Carvone decreases Ca2+ entry through L-type Ca2+ channels, reducing the cardiac contractility and intracellular Ca2+, and, therefore, presenting promising antiarrhythmic activity in the rat hearts.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; Cardiac; Monoterpenes; Rats
767