Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2017; 109(4): 370-375
Case 5/2017 – A 28-Year-Old Woman with Cor Pulmonale Due to Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Chronic Pulmonary Thromboembolism
DOI: 10.5935/abc.20170148
Clinical aspects
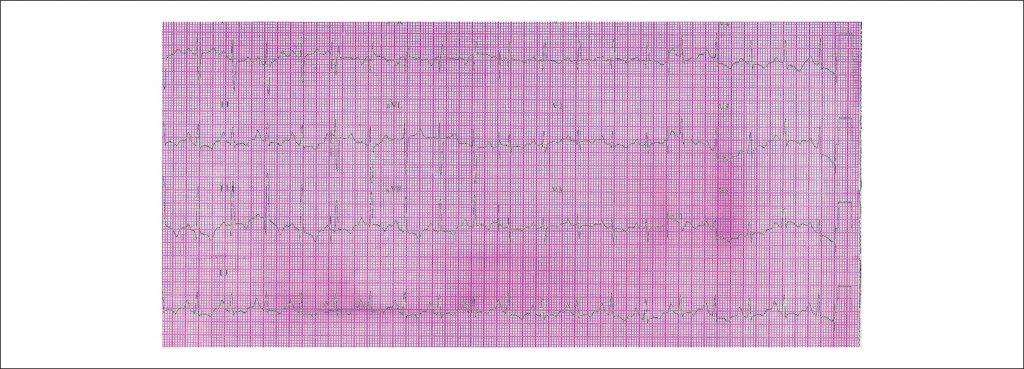
We report the case of a 28-year female patient denying any previous morbidity, who had acute PTE and progressively developed significant functional impairment and signs suggestive of chronic PTE during follow-up until death.
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is the third most frequent cause of cardiovascular disease in the general population, with an annual incidence of 100 to 200 cases per 100000 inhabitants, acute PTE being its most severe clinical presentation. The prevalence and incidence of spontaneous VTE in young adults are low, but increase significantly in the presence of risk factors, such as oral contraception use, obesity and thrombophilia, especially in associations. The use of oral contraceptives, such as estrogens/progestogens, increases by 2 to 4 times the risk of venous thromboembolic events. Activated protein C resistance is attributed to a mechanism related to higher risk for VTE in patients on oral contraceptives. In our case, the patient had been on regular use of oral contraceptives until the first event, but there is no information on their formulation. Obesity is considered a risk factor, increasing by 2.4 times the risk for VTE in obese individuals as compared to non-obese individuals. When associating obesity and oral contraceptive use simultaneously, the risk for VTE increases by 10 times. Significant thrombophilias, such as deficiencies in protein C, protein S and antithrombin, homozygosity for factor V Leiden and prothrombin gene mutation increase in up to 7 times the risk for venous thromboembolic events in patients on oral contraceptives. During the patient’s follow-up, certain thrombophilias, such as prothrombin gene mutation, hyperhomocysteinemia and antiphospholipid syndrome, were excluded, but neither factor V Leiden nor deficiency in natural anticoagulants were investigated.
[…]
1,132