Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2021; 116(1): 89-99
Cerebrovascular Disease Mortality Trend in Brazil (1996 To 2015) and Association with Human Development Index and Social Vulnerability
Abstract
Background
Cerebrovascular diseases (CBVD) are the second major cause of death in the world.
Objective
To analyze the mortality trend of CBVD in Brazil (1996 to 2015) and its association with Human Development Index (HDI) and the Social Vulnerability Index (SVI).
Methods
This is an ecological study. We analyzed the mortality rate standardized by CBVD. Death data were obtained from the Mortality Information System (SIM) and populational data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE). The model of regression by inflection points (Joinpoint regression) was used to perform the temporal analysis, calculating the Annual Percent Change (APC) and Average Annual Percent Change (AAPC), with 95% of confidence interval and a significance of 5%. Trends were classified as increasing, decreasing or stationary. A multivariate regression model was used to analyze the association between mortality by CBVD, HDI and SVI.
Results
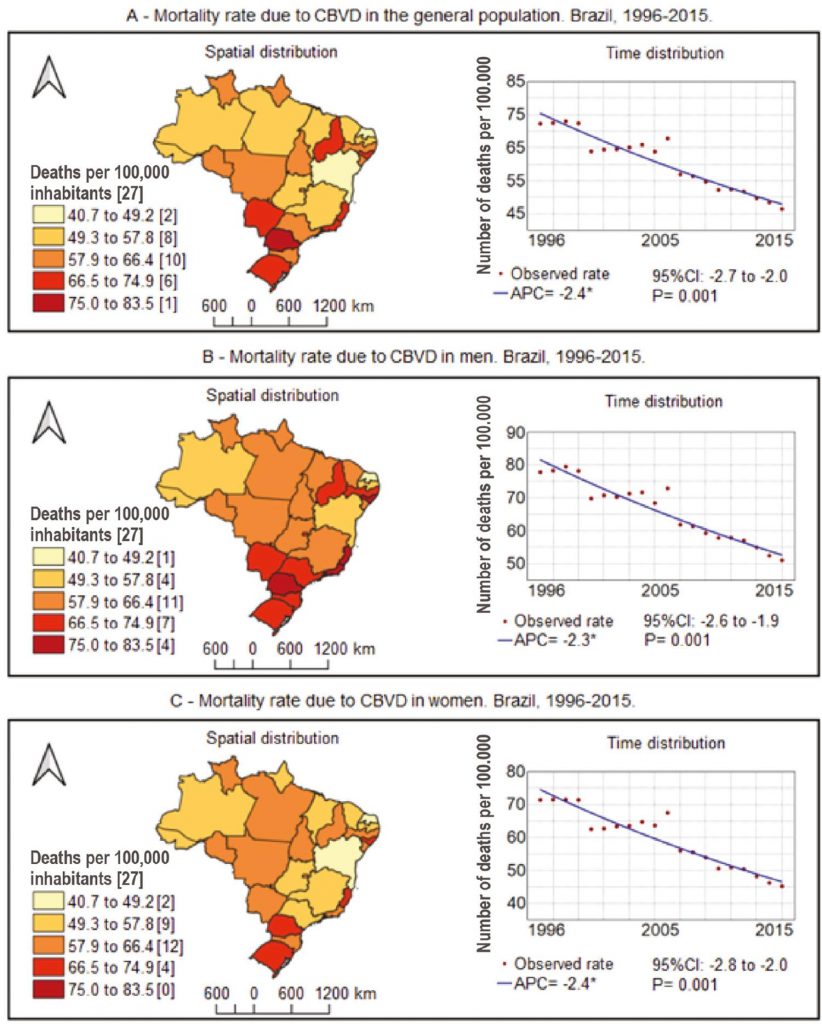
During this period, 1,850,811 deaths by CBVD were recorded. We observed a reduction in the national mortality rate (APC -2.4; p = 0.001). Twenty federation units showed a significant trend, of which 13 showed reduction, including all states in the Midwest (n=4), Southeast (n=4) and South (n=3). The HDI was positively associated and the SVI was negatively associated with mortality (p = 0.046 and p = 0.026, respectively).
Conclusion
An unequal epidemiological course of mortality was observed between the regions, being higher in the Southeast and South states, with a significative tendency of reduction, and lower in the North and Northeast states, but with a significative tendency of increase. HDI and SVI showed an association with mortality. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021; 116(1):89-99)
1,793