Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2023; 120(5): e20220467
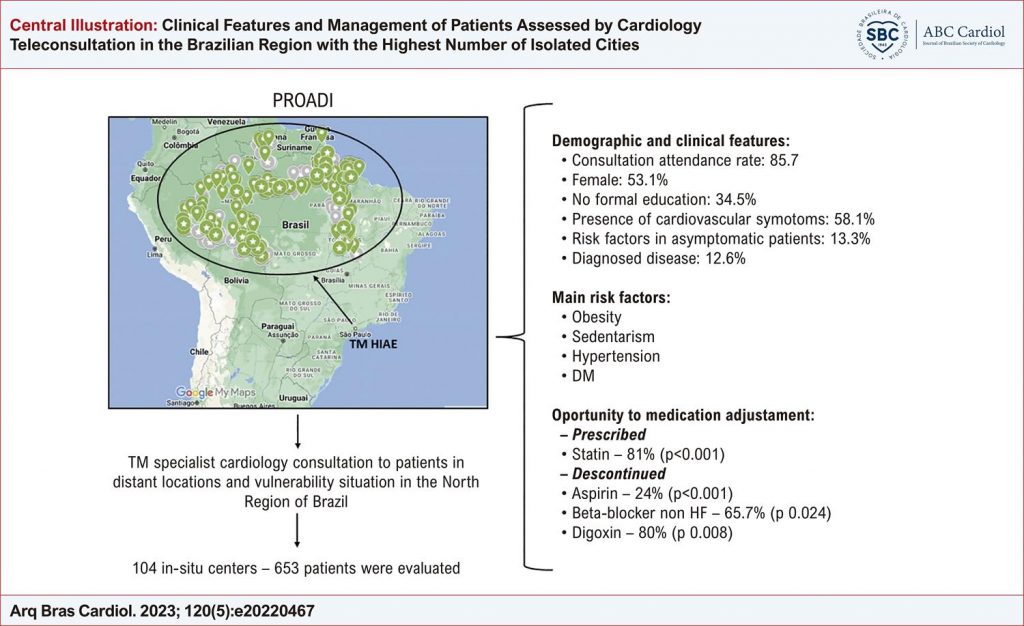
Clinical Features and Management of Patients Assessed by Cardiology Teleconsultation in the Brazilian Region with the Highest Number of Isolated Cities
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Telecardiology and its Potential in Remote Areas".
Abstract
Background
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of adult mortality. Geographically remote and low-income Brazilian regions lack specialized consultations. The telemedicine management of this population by cardiologists is not fully known.
Objectives
To analyze cardiology teleconsultation in the Brazilian region with the highest number of isolated cities.
Methods
From February 2020 to October 2021, patients from the North Region of Brazil evaluated by local general practitioners were referred for cardiological evaluation by telemedicine. Referral reasons, demographics, clinical history, physical examinations, tests, medications, and prescriptions pre- and post-telemedicine were analyzed (p<0.05 was considered statistically significant).
Results
We analyzed 653 patients. The attendance rate was 85.7% (53.1% female, mean age: 54.2±6.5 years). The main reasons for referral were cardiovascular symptoms (58.1%) and risk factors among asymptomatic patients (13.3%). Only 12.6% had a diagnosed disease. Most patients had regular physical examinations and electrocardiograms. Few had recent complementary tests. The prescription of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers and statins was significantly increased, while that of digoxin, noncardiac beta-blockers and acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) was decreased at the first teleconsultation. Most of the tests requested were of low complexity and cost: electrocardiogram (28.2%), chest X-ray (14%), echocardiogram (64.5%) and blood tests (71.8%). For 2.1% of patients, interventions were indicated, and 8% were discharged after the first consultation.
Conclusion
On-demand cardiology teleconsultation contributes to heart disease treatment optimization. Most patients were referred with syndromic diagnoses without previous complementary tests. The specialist workup requested was usually available locally and at a low cost but precluded early discharge. Local training could optimize the referral.
880