Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2022; 118(5): 894-902
Diagnostic Performance of Coronary Tomography Angiography and Serial Measurements of Sensitive Cardiac Troponin in Patients With Chest Pain and Intermediate Risk for Cardiovascular Events
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Role of Computed Tomography in Excluding Acute Coronary Syndrome: is Anatomy the Way?".
Abstract
Background
Coronary tomography angiography (CTA) has been mainly used for chest pain evaluation in low-risk patients, and few data exist regarding patients at intermediate risk.
Objective
To evaluate the performance of serial measures of sensitive troponin and CTA in intermediate-risk patients.
Methods
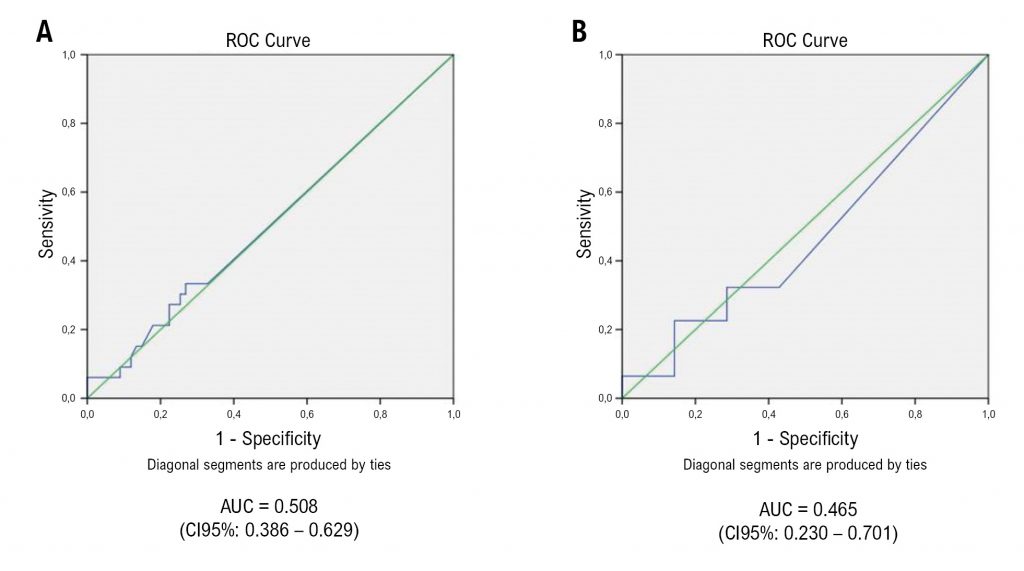
A total of 100 patients with chest pain, TIMI risk scores of 3 or 4, and negative troponin were prospectively included. All patients underwent CTA and those with coronary stenosis ≥ 50% were referred to invasive coronary angiography. Patients with coronary lesions <50% were discharged and contacted 30 days later by a telephone call to assess clinical outcomes. Outcomes were hospitalization, death, and myocardial infarction at 30 days. The comparison between methods was performed by Kappa agreement test. The performance of troponin measures and CTA for detecting significant coronary lesions and clinical outcomes was calculated. Results were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
Results
Coronary stenosis ≥ 50% on CTA was found in 38% of patients and significant coronary lesions on coronary angiography were found in 31 patients. Two clinical events were observed. Kappa agreement analysis showed low agreement between troponin measures and CTA in the detection of significant coronary lesions (kappa = 0.022, p = 0.78). The performance of CTA for detecting significant coronary lesions on coronary angiography or for predicting clinical events at 30 days was better than sensitive troponin measures (accuracy of 91% versus 60%).
Conclusion
CTA performed better than sensitive troponin measures in the detection of significant coronary disease in patients with chest pain and intermediate risk for cardiovascular events.
1,270