Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2020; 114(4): 730-731
Evolved Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction with Left Ventricular Pseudoaneurysm: A Diagnostic Dilemma
Introduction
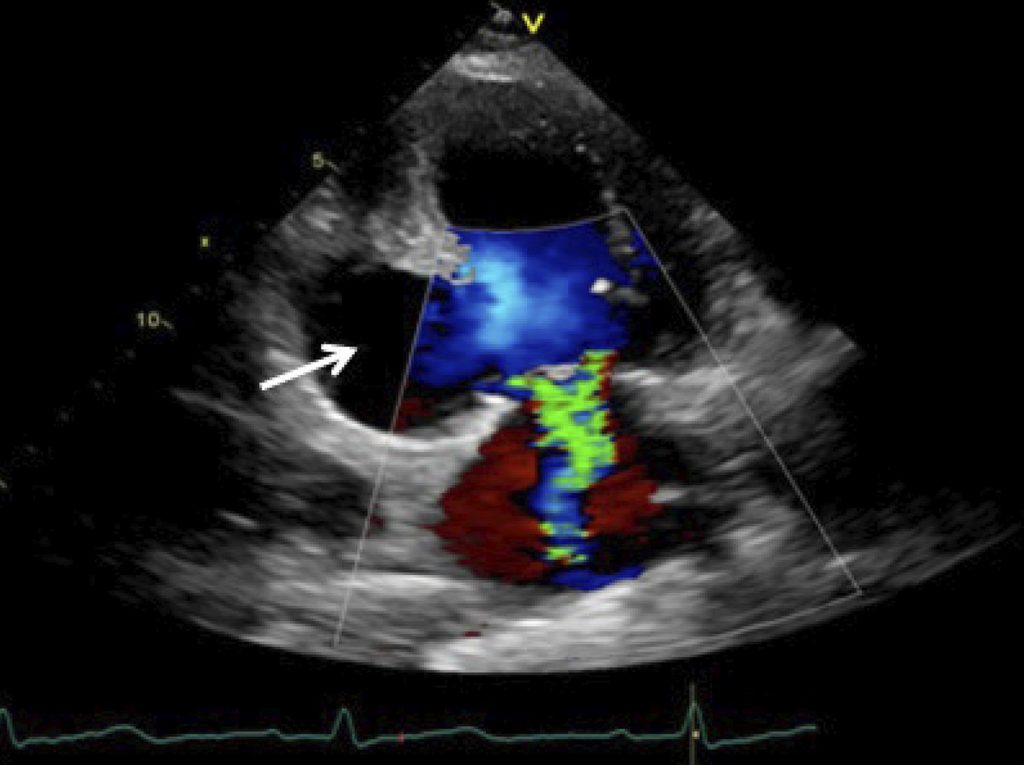
The left ventricular (LV) pseudoaneurysm (PA) is a rare mechanical complication of acute myocardial infarction (AMI). It results from myocardial rupture, in which the hemorrhagic process is contained by the adherent pericardium. It occurs most commonly in the inferior and posterior ventricular wall, since the rupture of the anterior ventricular wall usually leads to cardiac tamponade and immediate death, while the inferior-posterior face of the heart rests on the diaphragm, facilitating the ventricular cavity containment by the pericardium. – Imaging methods are crucial to establish the diagnosis. Transthoracic (TTE) and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) allow the definitive diagnosis in 26% and 75% of cases, respectively. , Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is useful in the differential diagnosis of LV PA and aneurysm, with a reported sensitivity of 100%. The presence of late pericardial enhancement in the CMR is highly suggestive of LV PA, which may represent the effect of the passage of blood into the pericardial space at the time of myocardial rupture, with subsequent pericardial inflammation and fibrosis. , ,
[…]
2,850