Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2024; 121(12): e20230837
High Power Short Duration Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Long-Term Predictors of Success and Recurrence – A Multivariate Analysis
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "High-power, Short-duration Radiofrequency Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: Point-by-Point or Catheter Dragging Technique?".
Abstract
Background
Point-by-point ablation with a high-power short-duration (HPSD) technique in atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation is used worldwide. Little data is available with the HPSD and dragging technique (DT).
Objective
To perform a multivariate analysis of clinical and procedural predictors of success and recurrence in HPSD with DT.
Methods
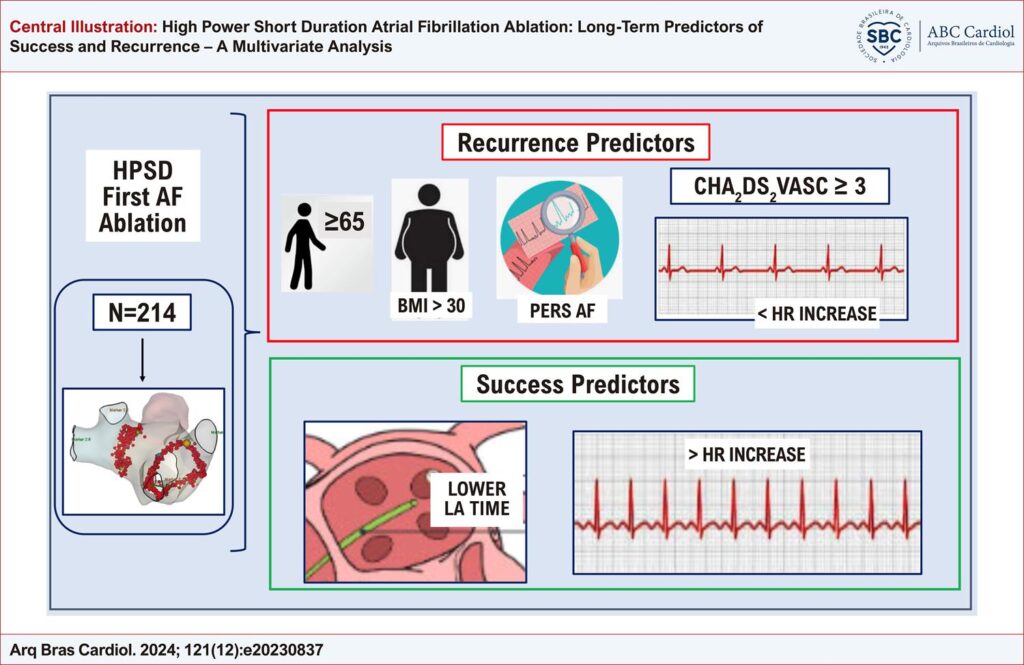
214 patients in the first AF ablation in sinus rhythm were prospectively enrolled. DT with radiofrequency power of 50 W and contact force (CF) of 10–20 g and 5–10 g at a flow rate of 40 mL/min were applied on the anterior and posterior walls, respectively. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
143 (66.8%) males, paroxysmal AF (PAF) in 124 (57.9%), with 61.1±12.3 years and followed for 32.8±13.2 months. After 90 days, AF occurred in 43 (20.1%) patients, 19 (15.3%) from PAF, and 24 (26.7%) in persistent AF (PersAF). Multivariate analysis indicated as clinical predictors of recurrence: age ≥ 65 years (p=0.006); obesity [body mass index > 30 (p=0.009)]; CHA2DS2VASC score ≥ 3 (p=0.003); and PersAF (p=0.045). The procedural predictor of recurrence was a heart rate increase < 10% (p=0.006). Predictors of success were an increase in heart rate ≥ 30% (p=0.04) and < 60 min in left atrium time (LAT) (p=0.007).
Conclusion
AF ablation with DT and HPSD clinical and procedural predictors of recurrence were ≥ 65 years, obesity, a CHA2DS2VASC ≥ 3, PersAF, and a heart rate increase of < 10% after ablation. Success predictors were an increase of ≥ 30% in heart rate and low LAT (< 60 min).
Keywords: Atrial Fibrillation; Catheter Ablation; Recidivism; Tachycardia
621