Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(6): e20240671
Naples Prognostic Score Predicts New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with ST-Elevated Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Primary Angioplasty
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Exploring the Naples Prognostic Score: A Key to Predicting New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in STEMI Cases".
Abstract
Background
New-onset atrial fibrillation (NOAF) is a typical complication in patients with ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI). Previous studies have investigated inflammation as a NOAF predictor. The Naples prognostic score (NPS) is a novel marker of inflammation and nutritional status.
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate the predictive power of the NPS for NOAF.
Methods
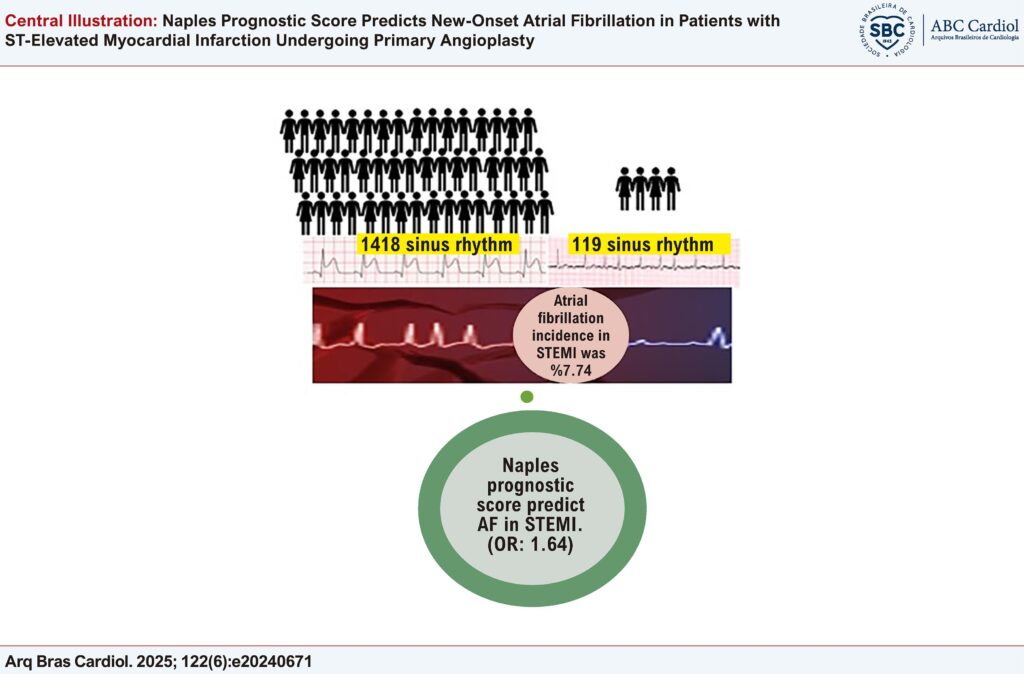
This study enrolled 1537 consecutive STEMI who underwent pPCI. The patients who presented NOAF during hospital admission and those who remained in sinus rhythm (RSR) were compared in terms of baseline characteristics. Univariate and multivariate analyses were carried out to identify variables predicting NOAF development, and p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
NOAF was detected in 7.74% (n: 119) of the participants. The mean age (67.03±13.48 vs 57.84±11.31; p <0.001) and NPS (2.53±1.17 vs 2.25±1.10, p=0.008) were significantly higher in the NOAF group. Multivariate analysis revealed age (Odds ratio [OR]: 1.045 for a year, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.019–1.071, p=0.001), NPS (OR: 1.645, 95% CI: 0.984–2.748, p=0.037) and left atrial dimensions (OR: 2.542 for cm, 95% CI: 1.488–4.342, p=0.001) as independent predictors of NOAF.
Conclusions
The NPS was an independent predictor of NOAF in STEMI patients, in addition to classical factors such as age and left atrial dimensions. This score, mostly related to an inflammatory burden, may help to predict NOAF incidence and select better potential therapies aimed at abating inflammation after myocardial infarction.
Keywords: Angioplasty; Atrial Fibrillation; Myocardial Infarction; Prognosis
299