Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2023; 120(12): e20230087
Non-Invasive Assessment of Cardiodynamics by Impedance Cardiography during the Six-Minute Walk Test in Patients with Heart Failure
Abstract
Background
The six-minute walk test (6MWT) is commonly used to evaluate heart failure (HF) patients. However, several clinical factors can influence the distance walked in the test. Signal-morphology impedance cardiography (SM-ICG) is a useful tool to noninvasively assess hemodynamics.
Objective
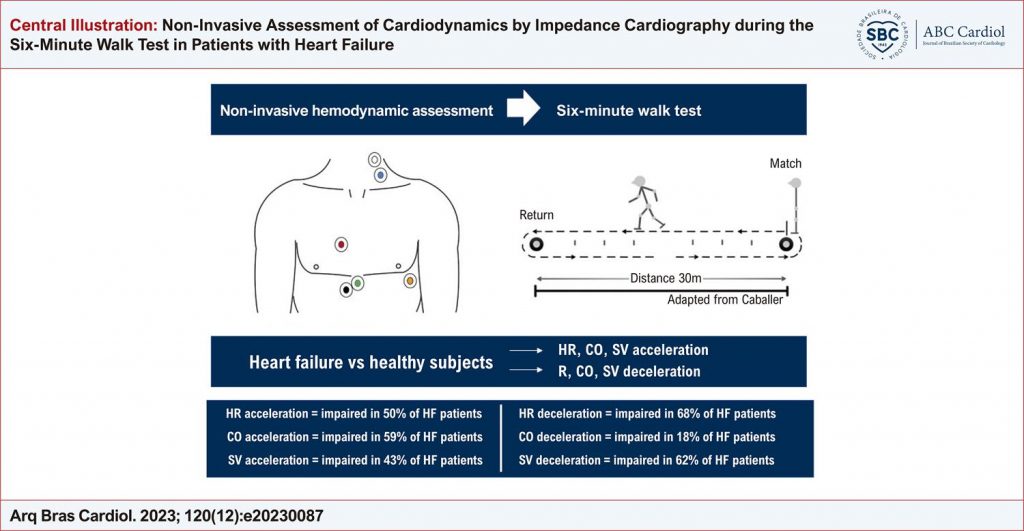
This study aimed to compare cardiac output (CO), heart rate (HR), and stroke volume (SV) acceleration and deceleration responses to 6MWT in individuals with HF and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and healthy controls.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional observational study. CO, HR, SV and cardiac index (CI) were evaluated before, during, and after the 6MWT assessed by SM-ICG. The level of significance adopted in the statistical analysis was 5%.
Results
Twenty-seven participants were included (13 HFrEF and 14 healthy controls). CO and HR acceleration significantly differed between groups (p<0.01; p=0.039, respectively). We found significant differences in SV, CO and CI between groups (p<0.01). Linear regression showed an impaired SV contribution to CO change in HFrEF group (22.9% versus 57.4%).
Conclusion
The main finding of the study was that individuals with HFrEF showed lower CO and HR acceleration values during the submaximal exercise test compared to healthy controls. This may indicate an imbalance in the autonomic response to exercise in this condition.
Keywords: Exercise Tolerance; Hemodynamics; Impedance Cardiography
797