Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(7): e20240885
Orientin Alleviates Oxidative Stress And Apoptosis In Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Via The Lncrna H19/Mir-103-3p/ALDH2/PI3K/AKT Axis
This Research Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Unraveling Pathophysiological Mechanisms via Non-coding RNAs".
Abstract
Background
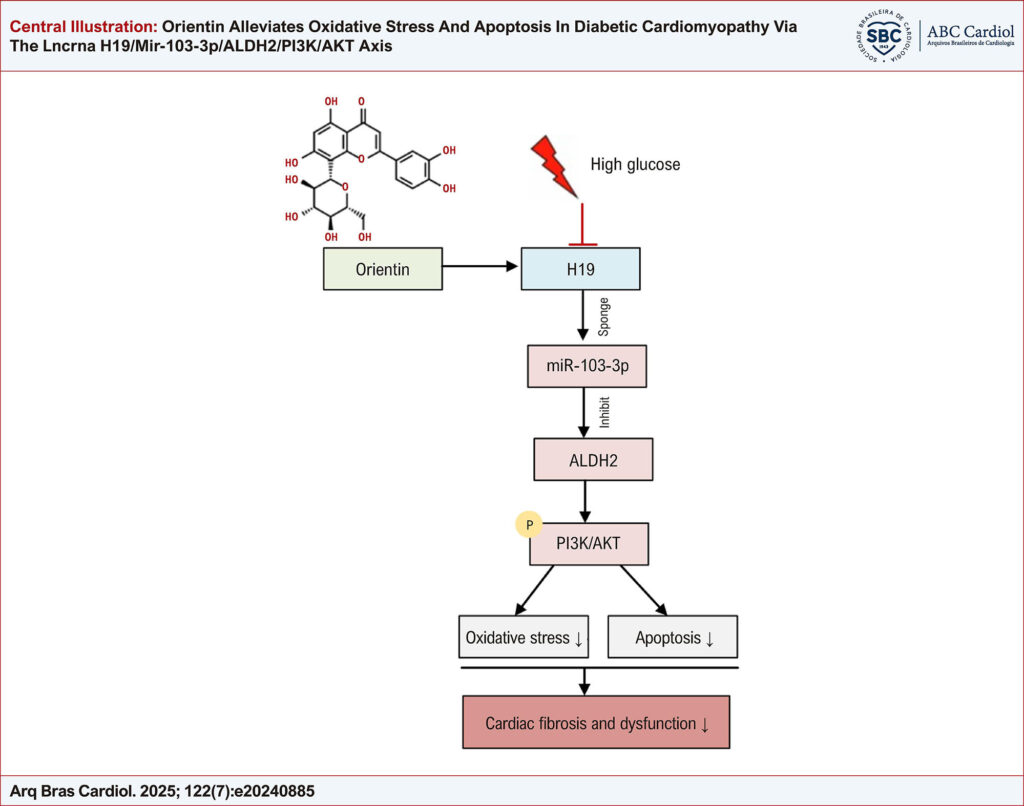
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is an irreversible cardiovascular complication of diabetes mellitus characterized by detrimental cardiac remodeling. Orientin, a water-soluble flavonoid present in many medicinal plants, exerts various pharmacological effects.
Objectives
To investigate the cardioprotective effects of orientin in diabetic conditions and elucidate the mechanisms associated with non-coding RNAs.
Methods
The streptozotocin-induced DCM model was established by a combined use of streptozotocin and a high-fat diet. Cardiac structure and function in diabetes mellitus mice were evaluated using histological and echocardiographic analyses. Masson, TUNEL, western blot, and ELISA in mouse hearts were performed to analyze cardiac fibrosis, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Expression levels of lncRNA H19, miR-103-3p, ALDH2, and PI3K/AKT-related proteins in mouse heart and HL-1 cells were evaluated using real-time qPCR or western blot. The significance level was set at p<0.05.
Results
Orientin improved cardiac function and ameliorated cardiac injury in diabetic mice. Orientin inhibited cardiac fibrosis, reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and increased the activities of antioxidant enzymes. In pathological conditions, H19 and ALDH2 levels were reduced while miR-103-3p levels increased, which were reversed by orientin. H19 upregulated ALDH2 expression by binding to miR-103-3p and activated the PI3K/AKT pathway in high glucose-treated HL-1 cells. H19 depletion or PI3K inhibitor reversed the effects of orientin on apoptosis and oxidative stress in HL-1 cells under high glucose conditions.
Conclusions
These findings reveal a protective mechanism of orientin in DCM, which involves the regulation of the H19/miR-103-3p/ALDH2/PI3K/AKT signaling axis, providing a potential strategy for treating DCM.
115