Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2022; 118(4): 768-777
Plasma Ceramides in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Stratification
Abstract
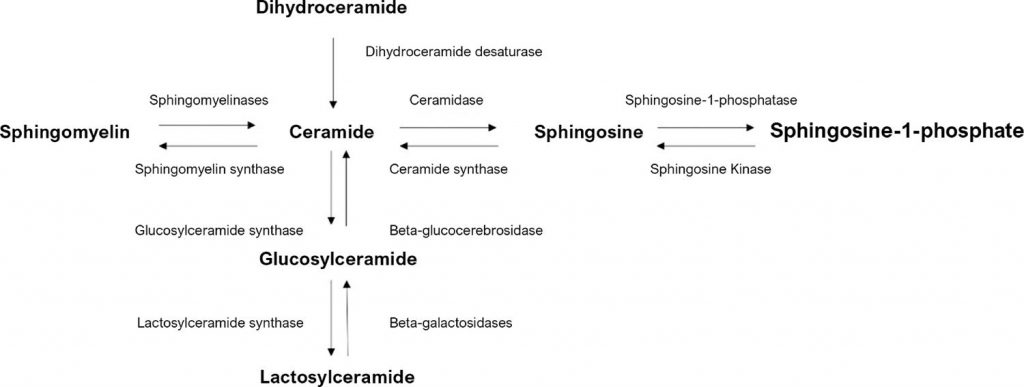
Ceramide production takes place throughout the body and plays a key role in the maintenance of normal physiology. However, ceramide levels are altered during disease states, particularly considering the development of diabetes and dyslipidemia. Ceramide production is also associated with atherosclerotic plaque instability. Recent studies revealed that patients with unstable coronary artery disease (CAD) presented increased plasma ceramide levels (especially C16, C18, and C24:1). These molecules are currently considered emerging biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), being used for predicting atherosclerotic plaque instability and adverse cardiovascular events independently from traditional risk factors. With the aim of describing and discussing the role of ceramides in the stratification of cardiovascular diseases, this narrative review contextualizes the importance of this biomarker in the present cardiology scenario.
1,269