Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(2): e20240420
Preoperative Predictors of Hospital Readmission within 5 Years Following CABG: Cohort Analysis of the REPLICCAR II Database
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Predictors of Hospital Readmission After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting – Reflections and Perspectives".
Abstract
Background
Reducing hospital readmissions following coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgeries is essential to optimizing medium- and long-term patient outcomes.
Objective
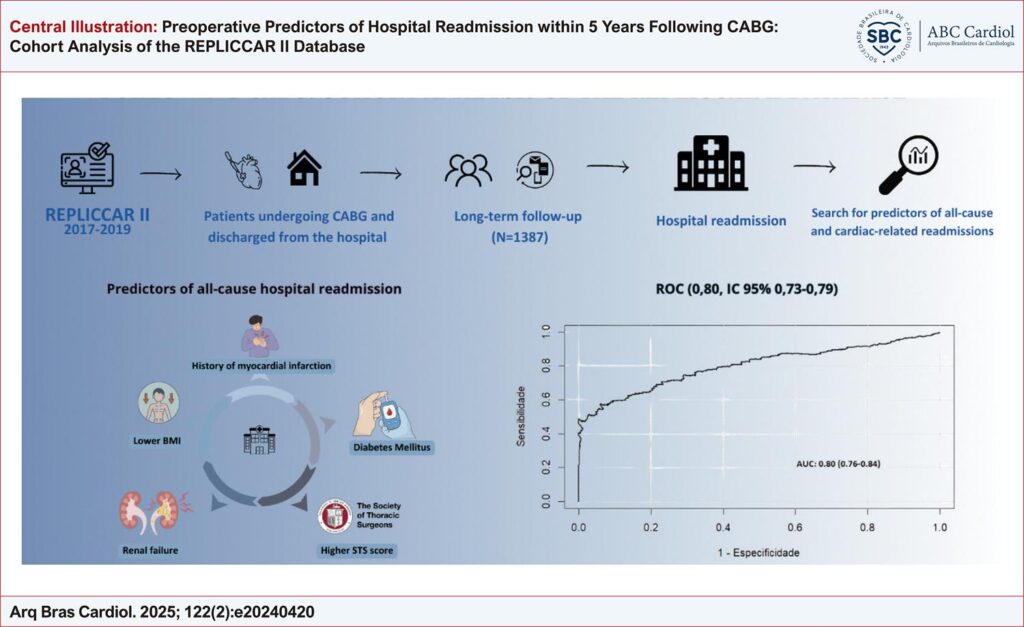
To analyze preoperative predictors associated with all-cause and cardiac readmissions within 5 years following CABG.
Methods
We analyzed 1,387 patients who underwent CABG between June 2017 and July 2019 using data from the multicenter REPLICCAR II registry. Follow-up was carried out by telephone interviews using a questionnaire structured in the REDCap platform. Statistical analysis included univariate and multivariate methods, with Cox regression and internal validation through calibration and discrimination tests. A significance level of 5% was applied.
Results
The cumulative incidence of all-cause readmission was 27.69%, with a mean follow-up of 4.3 years and a mean time to readmission of 2.4 years. Multivariate regression analysis indicated the following predictors of higher all-cause readmission risk: lower body mass index (HR=0.97, p=0.032), history of myocardial infarction (HR=1.27, p=0.024), diabetes mellitus (HR=1.35, p=0.004), renal failure (HR=1.62, p=0.004), and higher STS score (HR=1.22, p<0.001). A moderate correlation was observed between readmission and mortality (Rho=0.55).
Conclusions
This analysis demonstrates that lower body mass index, history of myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, renal failure, and elevated STS scores are significant predictors of increased hospital readmission risk following CABG.
368