Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(8): e20250047
Prognostic Value of Troponin to Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-associated Myocarditis
Abstract
Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-associated myocarditis is a rare but life-threatening immune-related adverse event (irAE). Cardiac troponin (cTn) and absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) have been reported to be associated with ICI-myocarditis.
Objective
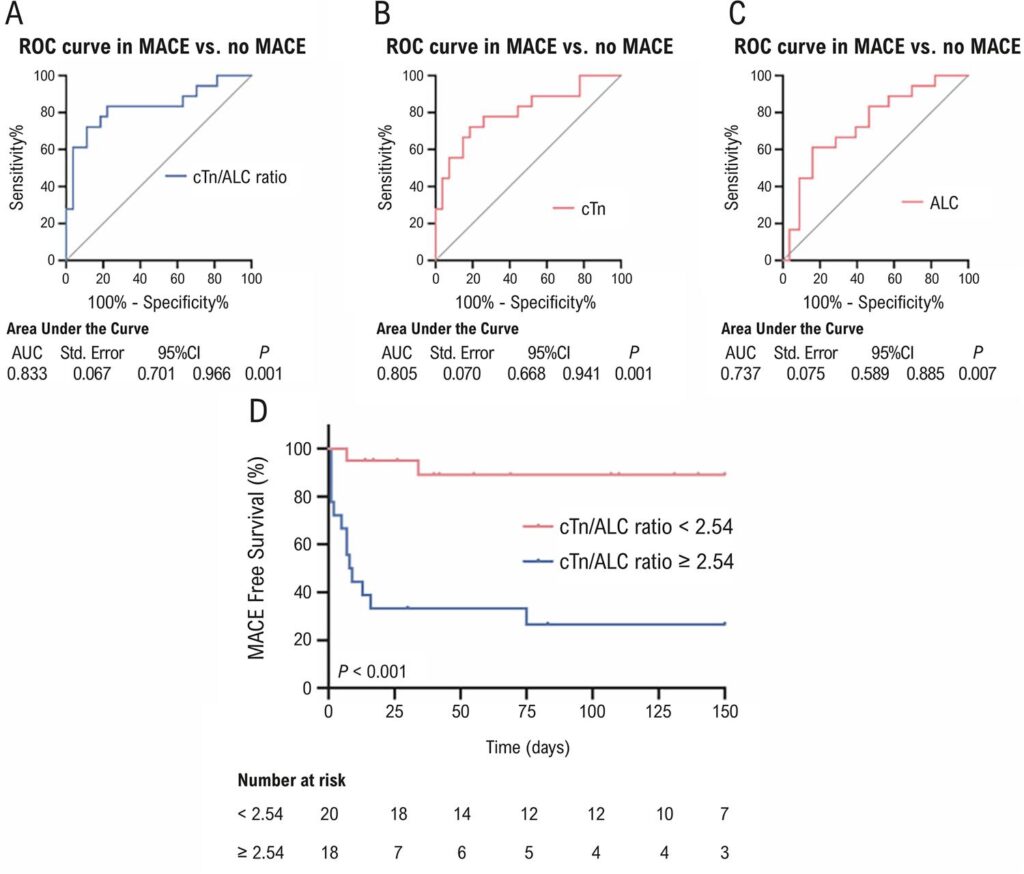
We aimed to investigate the prognostic value of the combination of these two features (cTn/ALC ratio) in ICI-associated myocarditis.
Methods
Our center performed a retrospective analysis of 46 patients with ICI myocarditis (cases) and 46 patients without myocarditis after receiving ICI (controls). We obtained data on cardiac enzymes, routine blood parameters, and other clinical biomarkers. Statistical significance was defined as a two-sided α level of 0.05. The association between these covariates and the clinical outcomes of ICI-mediated myocarditis was also tested.
Results
Abnormally elevated cTn (p < 0.001), cTn/ALC ratio (p < 0.001), and decreased ALC (p < 0.001) were observed in patients who developed ICI-myocarditis. The cTn/ALC ratio was associated with the development of severe myocarditis (OR, 5.05; 95% CI, 1.22-20.84; p = 0.025). Survival analysis and Cox regression analysis indicated that a higher cTn/ALC ratio emerged as a significant independent predictor for major adverse cardiac events (MACE) [HR, 5.64; 95%CI, 1.43-22.34; p = 0.014].
Conclusions
An increase in the cTn/ALC ratio was associated with the severity of ICI-myocarditis and could be an effective predictor of poor prognosis in patients with ICI-associated myocarditis.
Keywords: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors; Lymphocyte Count; Myocarditis; Prognosis; Troponin
130