Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2021; 116(6): 1169-1171
Pulmonary Arterial Intramural Hematoma Due to Acute Aortic Dissection
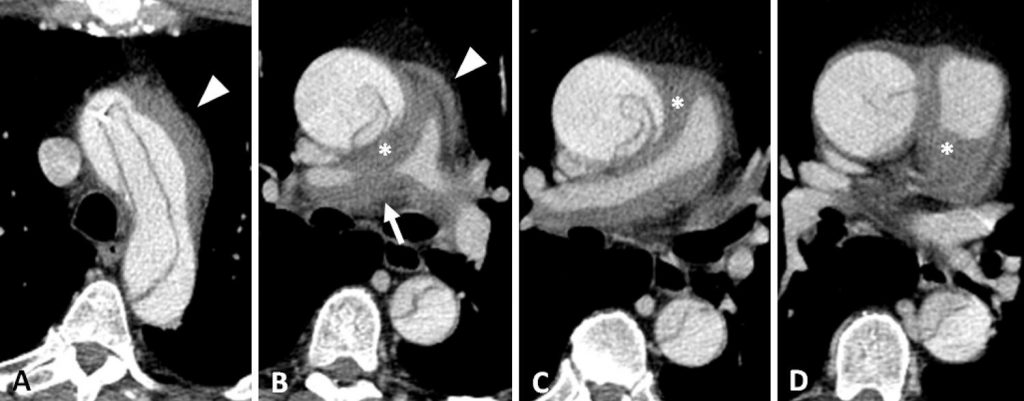
A 54-year-old male patient, who was a smoker, was admitted to the emergency room with acute chest pain and dyspnea. Investigation was initiated by means of computed tomography angiography of the chest, which showed extensive dissection of the thoracic aorta, beginning in the ascending segment (Stanford type A), associated with intramural hematoma of the pulmonary artery trunk and its main branches. It was more evident on the right, which determines local pulmonary luminal reduction, in addition to a small para-aortic and subaortic mediastinal hematoma. There were no signs of pulmonary thromboembolism, and the evaluation of the parenchyma showed no signs of pulmonary hemorrhage ( and ).
[…]
1,330