Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(7): e20240845
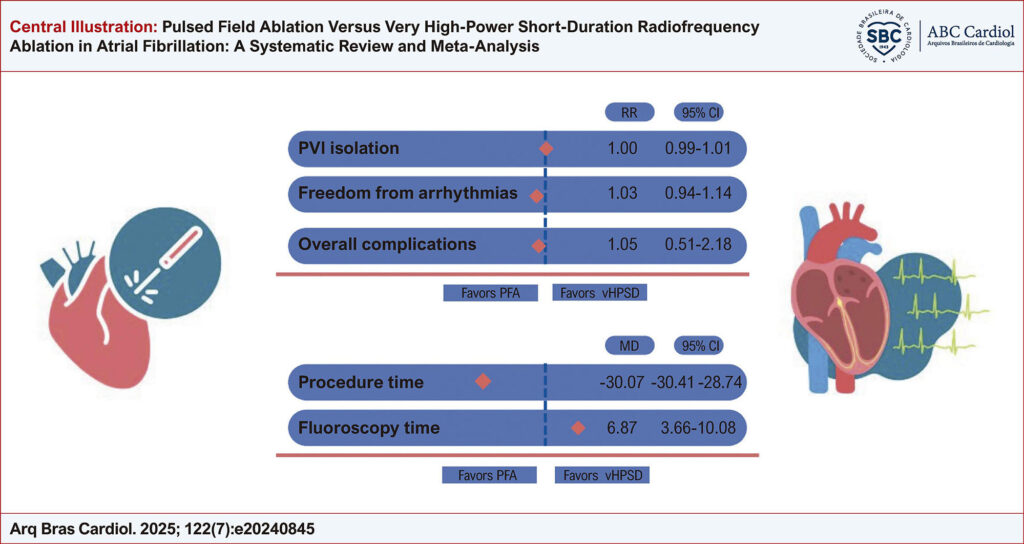
Pulsed Field Ablation Versus Very High-Power Short-Duration Radiofrequency Ablation in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Are We Still Looking for the Best Shot?".
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia, significantly impacts global healthcare due to its association with increased morbidity, mortality, and healthcare utilization., Catheter ablation has emerged as a cornerstone treatment for AF, offering rhythm control and symptomatic relief., Among contemporary ablation strategies, very high-power short-duration (vHPSD) radiofrequency (RF) ablation is valued for its efficiency and precision, while pulsed field ablation (PFA), a non-thermal technique utilizing electroporation, has gained attention for its potential to minimize collateral tissue damage.–
Since its introduction in Europe in 2021, PFA has been increasingly adopted for its promising safety profile, particularly in reducing the risk of complications such as pulmonary vein stenosis and damage to adjacent structures. However, despite these advancements, there remains a paucity of direct comparisons between PFA and vHPSD RF ablation, as existing studies are largely observational and retrospective in nature.– This lack of randomized controlled trials limits the ability to establish definitive comparative efficacy and safety profiles.
[…]
Keywords: Atrial Fibrillation; Catheter Ablation; Efficacy; Safety
301