Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2023; 120(12): e20220592
Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infection in Patients Undergoing Pediatric Cardiac Surgery
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Risk Factors for Surgical Site Infection after Pediatric Cardiac Surgery".
Abstract
Background
Surgical site infection is an important complication after pediatric cardiac surgery, associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
Objectives
We sought to identify risk factors for surgical site infection after pediatric cardiac surgeries.
Methods
A case-control study included patients aged between 1 year and 19 years and 11 months of age, submitted to cardiac surgery performed at a tertiary cardiac center from January 1 st , 2011, through December 31, 2018. Charts were reviewed for pre-, intra, and postoperative variables. We identified two randomly selected control patients with the same pathophysiological diagnosis and underwent surgery within thirty days of each index case. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify risk factors. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05.
Results
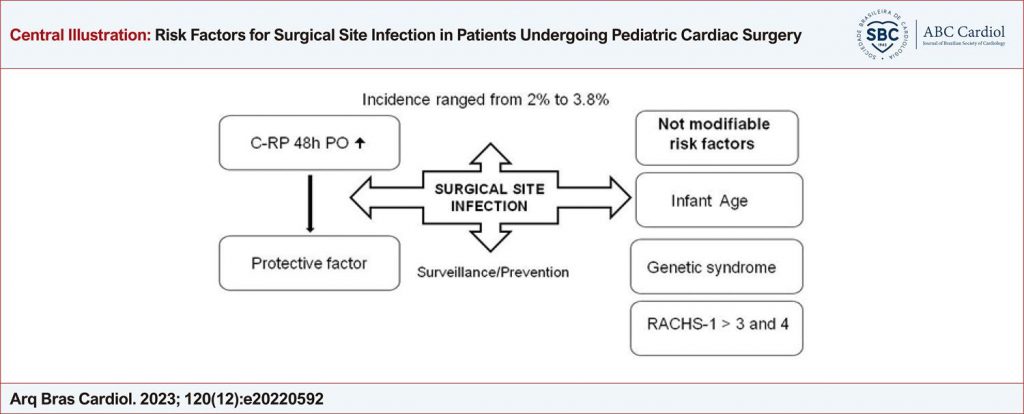
Sixty-six cases and 123 controls were included. Surgical site infection incidence ranged from 2% to 3.8%. The following risk factors were identified: Infant age (OR 3.19, 95% CI 1.26 to 8.66, p=0.014), presence of genetic syndrome (OR 6.20, CI 95% 1.70 to 21.65, p=0.004), categories 3 and 4 of RACHS-1 (OR 8.40, CI 95% 3.30 to 21.34, p<0.001), 48 h C-reactive protein level range was detected as a protective factor for this infection (OR 0.85, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.98, p=0.023).
Conclusions
The risk factors defined in this study could not be modified. Therefore, additional surveillance and new preventive strategies need to be implemented to reduce the incidence of surgical site infection. The increased CRP in the postoperative period was a protective factor that needs further understanding.
1,532