Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2024; 121(12): e20230783
Short-term Oral Nitrite Administration Decreases Arterial Stiffness in Both Trained and Sedentary Wistar Rats
This Original Article is referred by the Short Editorial "Nitrite Supplementation Attenuates Vascular Stiffness Independently of Physical Exercise".
Abstract
Background
Nitric Oxide (NO) plays an important role in blood pressure (BP) regulation, acting directly on peripheral vascular resistance through vasodilation. Physical training (via eNOS/NO) and intake of nitrite have been considered major stimuli to increase NO.
Objective
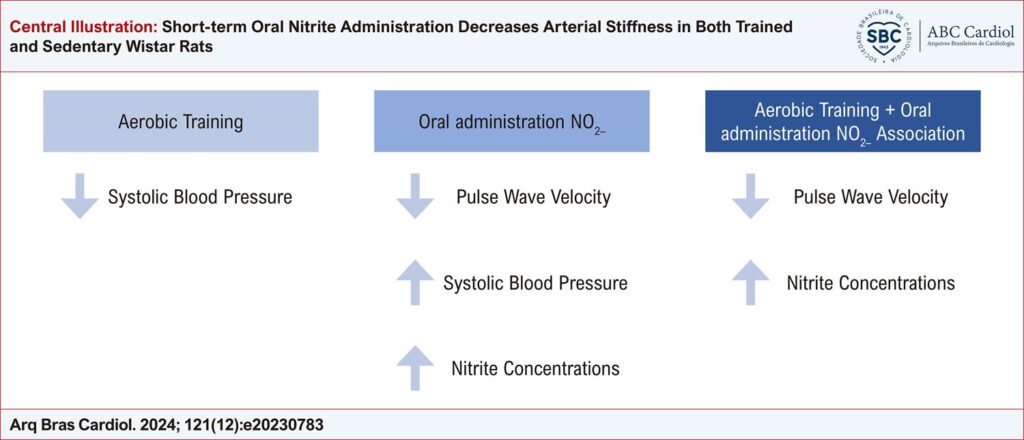
We examined the effects of oral nitrite administration and aerobic exercise training on BP and arterial stiffness in Wistar rats.
Methods
Thirty-nine (39) young male Wistar rats were divided into the following groups (n = 9 or 10 per group): Sedentary-Control (SC), Sedentary-Nitrite (SN), Trained-Control (TC), and Trained-Nitrite (TN). They were submitted to aerobic physical training on treadmills for 8 weeks (50-60% of physical capacity, 1h/day, 5 days/week) or kept sedentary. In the last 6 days of training, oral nitrite was administered (15 mg/Kg by gavage). BP, arterial stiffness, and plasma and tissue nitrite concentrations were assessed after the training and oral nitrite administration period. The significant level was defined as p < 0.05.
Results
Oral administration of nitrite was effective in reducing arterial stiffness values (TN, -23%; and SN, -15%). Both groups that had only one type of intervention showed lower systolic BP compared with control (TC vs. SC, -14.23; and SN vs. SC, – 12.46).
Conclusion
We conclude that short-term oral administration for 6 days and an aerobic physical training program promote several hemodynamic benefits in male Wistar rats, such as improvements in arterial stiffness and BP. These responses suggest that physical training and sodium nitrite supplementation can be alternatives for the prevention and treatment of hypertension.
Keywords: Exercise; Hypertension; Nitric Oxide; Nitrites; Physical Exercise; Pulse Wave Analysis
338