Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2025; 122(5): e20240821
TIMI Risk Score for Secondary Prevention to Risk Stratify Chronic Coronary Syndrome Patients: External Validation Study
Abstract
Background
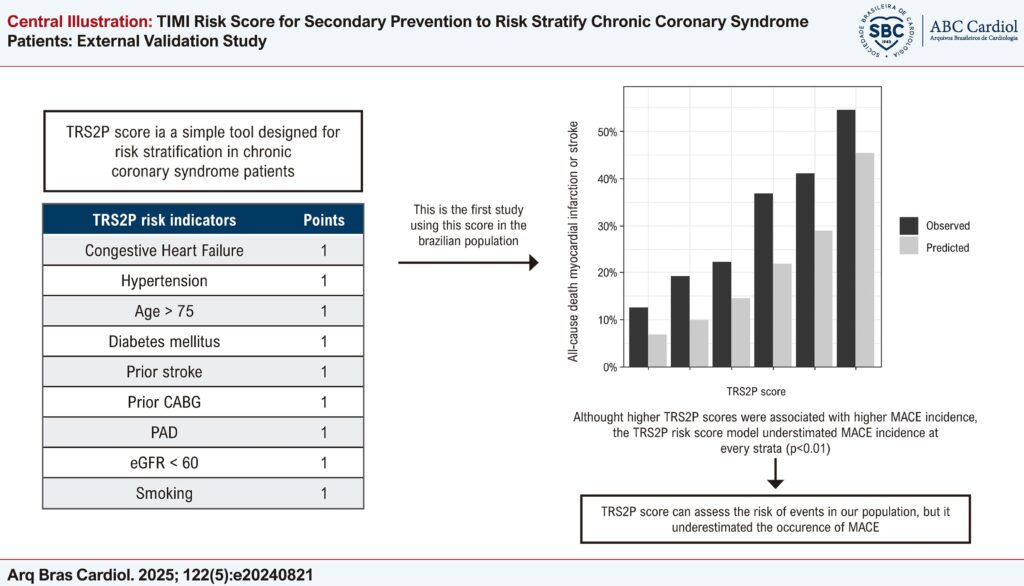
Risk stratification in chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) patients is challenging. TIMI Risk Score for Secondary Prevention (TRS2P) is a simple nine-point tool developed to predict cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), and ischemic stroke among post-MI patients. No studies have been conducted on it in the Brazilian population.
Objective
Validate the TRS2P score among CCS patients at a tertiary center in Brazil.
Methods
This is a registry-based study of patients with CCS, defined as having a previous revascularization procedure, previous MI, or ≥50% stenosis in at least one epicardial coronary artery. The primary outcome was the three-year incidence of MACE (death, MI or stroke). The predicted risk was as reported in the original derivation study. Calibration was assessed through a calibration plot and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test. Discrimination was evaluated through the concordance (C)-statistic. A significance level of 0.05 was adopted.
Results
The study sample consisted of 515 patients. There were 173 (34%) women, 75 (15%) aged over 75 years, 298 (58%) had diabetes, and 156 (30%) had chronic kidney disease. During follow-up, 126 MACE were documented. The estimated three-year incidence was 24% (95% confidence interval [CI] 21%-28%), whereas the predicted incidence was 15%. Although higher TRS2P scores were associated with higher MACE incidence, the TRS2P risk score model underestimated MACE incidence at every strata (p < 0.01). The C-statistic was 0.64 (95% CI 0.58-0.69).
Conclusion
The TRS2P score identifies patients with a higher risk of cardiovascular events but it underestimated MACE and presented poor discrimination in a Brazilian CCS cohort.
733