Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2023; 120(1): e20220878
Revisiting the QT Interval: An Old Marker for a New Disease?
This Short Editorial is referred by the Research article "Prolongation of the QTc Interval at Admission is Associated with Increased Mortality in Patients with SARS-COV-2 during Hospitalization".
The SARS-Cov-2 (Covid-19) infection had its first cases reported in December 2019 in China and quickly spread worldwide, being announced as a pandemic in March 2020 by the World Health Organization. Respiratory manifestations are classic; however, cardiovascular complications can occur due to an indirect cardiac involvement or a direct action of the virus in the myocardial tissue. Consequently, we can find heart failure, myocarditis, arrhythmias, and cardiogenic shock.
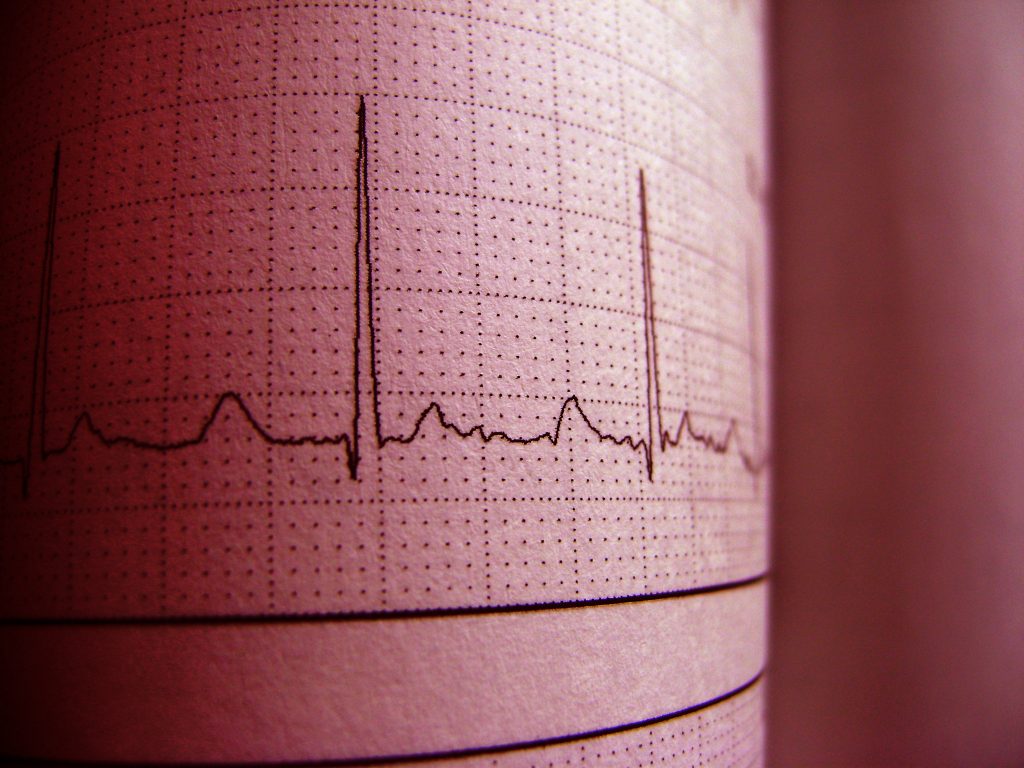
The QT interval, measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave, represents the process of ventricular depolarization and repolarization and varies with heart rate. Normal values for the corrected QT interval (QTc) would be≥450 ms in men and≥460 ms in women. Prolongation of the QTc interval≥500 ms is strongly associated with the occurrence of malignant arrhythmias and sudden death. Every 10 ms of QTc interval increment, there is a 5 to 7% increase in the risk of torsade de Pointes (TdP); every 20 ms, there is a substantial imminent risk.
[…]
Keywords: Long QT; Long Qt Syndrome; QT interval
2,974